The National Academy of Sciences are about to publish an article in their proceedings entitled ‘Privacy In The Age Of Augmented Reality’, co-authored by Alessandro Acquisiti, Ralph Gross and Fred Stuzman. It is about developments in face recognition software.
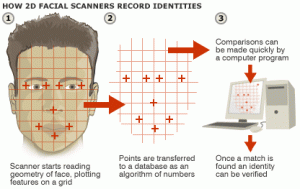 To use the authors’ words the document
To use the authors’ words the document
“investigate(s) the feasibility of combining publicly available Web 2.0 data with off-the-shelf face recognition software for the purpose of large-scale, automated individual re-identification.”
They are also working on an app that can do it all from your phone! See the FAQ section here for more information. The article reports a series of experiments conducted over the last year or so during which the researchers try to identify a person from their photo using an over the counter face recognition software using information that is freely available over the internet.
The results are interesting. The experiments are as follows:
Students walking through the university campus were asked if their photo could be taken and to complete a questionnaire. As they were answering the questions the computation task was carried out, looking for a picture match on Facebook and requiring only seconds. In this case more than 30% of the students were immediately traced.
Because the faces were the same but the photos taken from different angles, humans had to decide which of the possible matches were the most appropriate, but that is not always the case. Some photos are replicated and therefore the computer can give a 100% guarantee that the match is correct.
For example in another experiment the researchers used an online dating agency that provided anonymous photos. In this case they could match names to the photos in about 10% of cases. In several cases the same photo had been used on different sites.
In a third experiment the knowledge gained was used to search for further private information, all freely available on the web, such as details of sexual preference, date and place of birth and this information even allowed them to generate the first five figures of the individual’s US social security number.
So it seems that we can draw a simple conclusion here, either now or in the very near future, as these technologies are improved and made freely available, anybody will be able to recognize anybody they see on the street, identify them through an app in their telephone, and find out about their interests and other personal information, if they have ever posted (or had posted for them) a photo of themselves on the internet.
For more information, please read my face recognition article on the Bassetti Foundation website.