Most scientists agree that the Earth is warming, whether due to the effects of human habitation and lifestyle or as part of a cycle that is as natural as the rotation of the Earth itself. Whatever the cause it looks as if sea levels are going to continue to rise, weather patterns are changing and this is going to cause serious problems for millions of people across the globe. But what can be done about it?
Firstly I should define the terms used both here and elsewhere a little better. Climate Change and Global Warming are the two main terms we hear in both the scientific and popular press. They are not however interchangeable. Climate change represents changes in the climate (obviously), increased or decreased rainfall for example as well as temperature change, but from a geographical point of view. Global warming specifically represents the increase in the Earth’s surface temperature in general as provoked by the increase in so called ‘greenhouse gas’ emissions, it is not geographical but global. This article on the NASA website describes the development of the terminology.
Global warming is therefore the tricky term. Recently however a group of scientists that included global warming skeptics agreed that the planet is in fact warming, although there is still some debate as to why. The results were a surprise as the research was carried out by a long time global warming skeptic at the University of Berkley, and reported to Congress last year. Read the article in the Los Angeles Times.
Those scientists that have accepted the definition of the problem have offered various engineering solutions to the problem, some seem a little absurd and others foolishly simple, so I would like to have a look at a few of them.
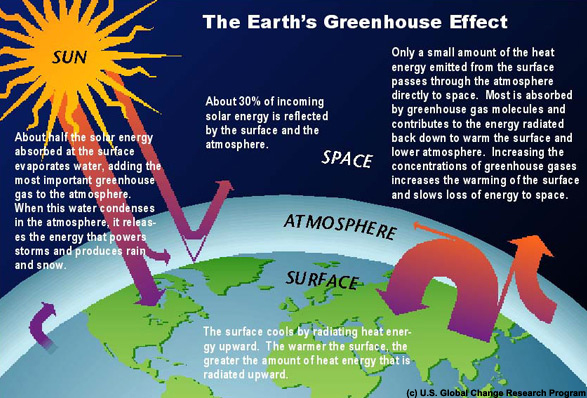
The following describes the problem of the ‘greenhouse effect’ that is believed to cause global warming, and the two main variables that could be manipulated, heat coming in and heat leaving the atmosphere.
Those in the know call it Geo-engineering, and its intentions and goals can be grouped into 2 basic classes, carbon dioxide removal techniques and solar radiation management techniques. The first involves the removal of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere through means such as ocean fertilization, changes in land use, afforestation, bio-energy, enhanced weathering and direct mechanical air capture techniques. This should let more heat out. The second involves surface albedo, cloud enhancement, stratospheric aerosol and space based methods. The first addresses the perceived cause of the problem, carbon and other pollutants in the atmosphere, while the second attempts to alleviate the problem by reflecting some of the heat from the sun back into space.
In terms of removing the carbon dioxide from the atmosphere they have a couple of large scale proposals, either land or sea based. Land based involve the obvious stuff like reforestation and stopping deforestation, also enhanced weathering techniques that involve spreading minerals on agricultural land to help the earth absorb the carbon as it is washed down by the rain, but also some interesting large scale engineering projects. One is to build lots of huge carbon alkali filters, probably above disused mines or in a desert somewhere and filter out the carbon as the air passes through them, before storing it in the chambers left by the mining. This technique is touted as interesting because the facilities can be built anywhere, and so cheap unpopulated zones can be used.
Ocean fertilization is another option being looked into, the oceans are fertilized with algae that soak up the carbon and sink down into the sea where the water then breaks it down. From a personal point of view I think the possibility of forever changing the oceans’ ecosystem is clear for all to see however (there is also a possibility that the volume of the seas might expand, not a desired side effect by any stretch of the imagination).
The second options are more interesting, they involve reflecting the sun’s rays back before they arrive, or reflecting more as they hit the Earth.
I like the simple ideas. Seeing as black soaks in more heat and white reflects it back into space, painting all rooves white and making all the roads white would do a great deal. As would growing light coloured plants in large numbers. Suggestions include planting huge areas of light coulored trees, a doubly productive approach. These ideas seem more reasonable to me as at least they can be managed relatively easily, something that cannot be said for ocean fertilization or some of the following suggestions.
One of which is to disperse millions of tiny pieces of reflective paper into the outer atmosphere so that less sun physically arrives. This seems a bit risky to me though as you can’t get rid of them once they are up there and the effect may be disastrous for some regions that could experience dramatic weather changes. Irreversibility is a big no as far as I am concerned, as is complete lack of control. In the event of the Earth starting to cool how could you get them down?
Artificial cloud production or whitening is also on the table, but also has the problem of control, you cannot determine where the clouds will go, and their very existence in one area can have huge impacts on others. If it rains too much in one place it may well cause drought in others. Stratospheric aerosol use poses similar risks and problems. Placing huge seas of mirrors in the desert to reflect the sun back up seems a bit less risky to me, maybe they could even produce some electricity while they were at it!
The solutions above do not address the problem of carbon emissions, and many seem to be rather haphazard operations. Many of them will be outside human control even during testing operations, and I can’t help but feel that they are talking about point of no return.
If you were wondering, I promise you that I did not make any of this stuff up, and if you would like to read an in depth report about the proposals outlined above you can download one here from the Royal Society of Engineering for free. More of my writing on this subject as well as many related issues can be found as ever on the Bassetti Foundation website.
If anybody else has any ideas I would love to hear them. Next week I look at the Holy Grail, pollution free, cost free energy, patented, on sale, and for you to behold from the comfort of your own computer.