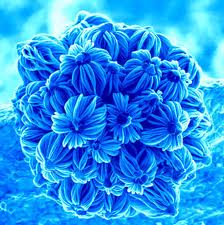
A couple of weeks ago whilst writing about nanotechnology and the associated risk involved in such engineering techniques I mentioned Nanoart. This week I would like to expand and to present a gallery of examples.
To quote Cris Orfescu, founder of Nanoart 21, “NanoArt is a new art discipline at the art-science-technology intersections. It features nanolandscapes (molecular and atomic landscapes which are natural structures of matter at molecular and atomic scales) and nanosculptures (structures created by scientists and artists by manipulating matter at molecular and atomic scales using chemical and physical processes). These structures are visualized with powerful research tools like scanning electron microscopes and atomic force microscopes and their scientific images are captured and further processed by using different artistic techniques to convert them into artworks showcased for large audiences.”
One of the issues raised during discussion in my previous posts was about the usefulness and point of such artistic expression, so here I quote the NanoArt 21 website:
“The purpose is to promote NanoArt worldwide as a reflection of a technological movement… a more appealing and effective way to communicate with the general public and to inform people about the new technologies of the 21st Century. NanoArt is aimed to raise the public awareness of Nanotechnology and its impact on our lives”.
There are several organizations that promote this form of expression and at least one international competition that offers cash prizes for the best examples (NanoArt 21 have an international competition). The German Centre for Research and Innovation hosted an exhibition of their collection in New York in 2011 and the number of artist/scientists involved seems to be growing.
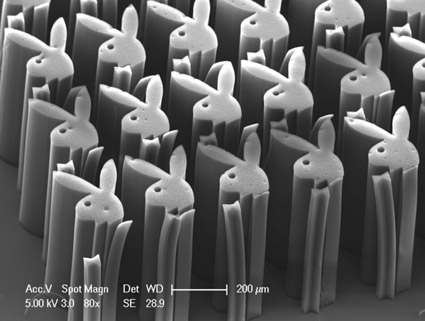
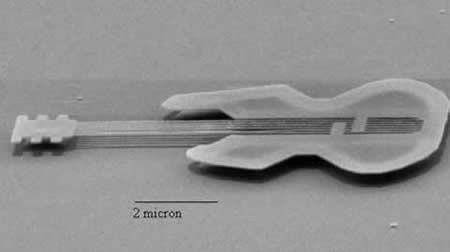
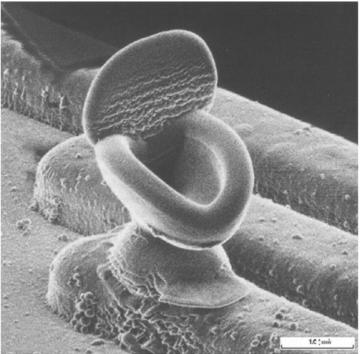
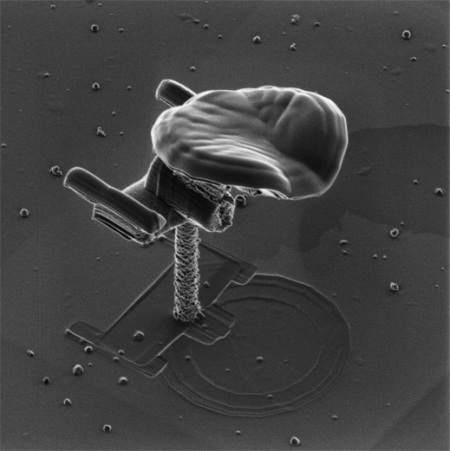
The following gallery should give you an idea of this particular art form. Also take a look at the Nanobama here. The image is of nanotubes made in the shape of President Obama’s face, similar in style to the playboy above.
You can find many other examples online. Do you like them? I personally like the 3D effect. It seems more accentuated because the images are created by electrons (electrically charged particles) rather than photons (particles of light). The electrons penetrate deeper into the structure creating images with more depth.