This is the 200th article I have written on Technology Bloggers! I really enjoy writing for the blog and value the community. ![]()
Technology Bloggers top smartphone app reviewers are without a doubt, Steve and Ron. In the past I have attempted app reviews myself, however I have never reviewed just a single application in one post. What better time to try something new then than in post 200!
I’m playing it safe with my first app review, and choosing an app that has already been reviewed by TechCrunch, and written about on the The Wall Street Journal’s website. The app is called Givit Video Editor, and is available for all iDevices.
What is Givit?
So what exactly is Givit Video Editor? Well in the words of (the apps creators) Vmix Media:
“Givit is a free, fun and simple app to quickly make and share great videos on iPhone.”
As I am sure you know, Instagram is a photo sharing application, which lets you share photos you take, pretty much instantly, to Facebook, Twitter and Tumblr. Givit offers a similar service, but for video.
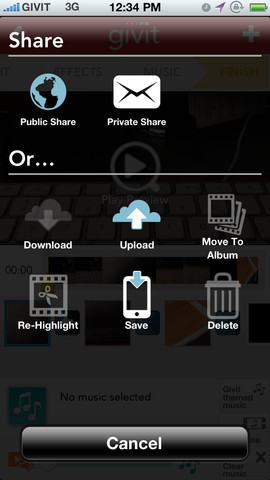
Sharing
One of the key features of the app is its sociability. The app interoperates ‘one-click’ sharing to Facebook, Twitter and YouTube, as well as email compatibility, so you can privately email clips. You can also upload your videos to the Givit cloud, where you get 5GB of free storage.
The latest version of the app (3.2.0) enables you to find and invite your Facebook friends, so you can see which of them are sharing their videos, and post your clips to your stream.
Features
The app is a clever video editor, which lets you mash different clips together, so you can chip and chop the best bits of clips and the stitch them together to make great montages.
The app is also compatible with live editing, so you can modify clips as you are filming, adding effects and music wherever you choose.
Cost
One of the best things about the app is that it is completely free! With the Standard Account (as I mentioned earlier) you get 5GB of permanent free storage; so long as you use it once every 3 months. 5GB is enough room to store around 30 minutes of uncompressed HD video; Givit probably have some clever compression going on, so I would imagine you get a bit more that 30 minutes.
Half an hour is all I think I need, as the clips I want to share are only usually a minute or two long, however if you are a budding videographer and need more space you can buy a Premium Account, which costs $29.99 a year, for an extra 100GB of storage.
So far, reviews of the app seem positive. The apps official iTunes rating is currently 4 stars in the UK store and 3.5 in the US store. Coverage on sites like Macworld, CNET and the above mentioned TechCrunch indicate the growing popularity of the service.
Interested in getting the app? Click here to download the Givit from iTunes.
Shoot, edit, share and store – that’s Givit!